Effectiveness and Efficiency of Lithium Dodecyl Sulfate (LDS) vs. Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate (SDS)
When comparing Lithium Dodecyl Sulfate (LDS) and Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate (SDS) in terms of effectiveness and efficiency, it’s essential to consider how these surfactants perform across various applications and contexts. Below is a detailed exploration of their effectiveness and efficiency:
- Surfactant Performance:
SDS:
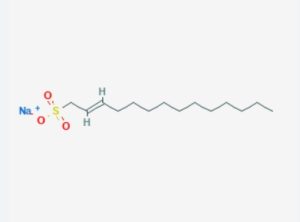
Micelle Formation: SDS is known for its ability to form micelles at relatively low concentrations, with a well-documented critical micelle concentration (CMC) of about 8.2 mM in water at 25°C. This makes it highly effective in reducing surface tension and acting as a detergent.
Cleaning Efficiency: SDS is highly effective in emulsifying oils, fats, and hydrophobic substances, making it a popular choice for cleaning and detergent formulations.
LDS:
Micelle Formation: The CMC of LDS may differ due to the presence of lithium ions, potentially altering its effectiveness in micelle formation. This could impact its efficiency in applications requiring micelle formation.
Cleaning Efficiency: While LDS can also emulsify hydrophobic substances, its performance might vary compared to SDS due to differences in ionic properties and micelle formation.
- Protein Denaturation and Biochemical Applications:
SDS:
Protein Denaturation: SDS is highly effective in denaturing proteins by disrupting non-covalent bonds, which is crucial for techniques like SDS-PAGE. It imparts a uniform negative charge to proteins, facilitating size-based separation.
Repeatability and Consistency: Due to its well-characterized behavior, SDS provides consistent and repeatable results, making it a reliable choice for many laboratory protocols.
LDS:
Protein Denaturation: LDS can also denature proteins, but the presence of lithium might affect the extent and manner of denaturation, potentially making it more or less effective depending on the specific protein and application.
Specialized Applications: LDS might offer unique advantages in certain biochemical applications where lithium ions provide beneficial interactions or stabilization.
- Efficiency in Cleaning and Detergent Formulations:
SDS:
Foaming and Detergency: SDS is known for its strong foaming properties and high detergency, making it effective in household and industrial cleaning products.
Cost-Effectiveness: SDS is widely available and cost-effective, contributing to its popularity in commercial products.
LDS:
Foaming and Detergency: LDS may exhibit different foaming and detergency properties due to the lithium ion. It could be more efficient in specific formulations where lithium-based surfactants outperform sodium-based ones.
Cost Considerations: LDS might be more expensive or less readily available than SDS, impacting its cost-effectiveness in large-scale applications.
- Environmental Impact:
SDS:
Toxicity and Biodegradability: SDS can be toxic to aquatic life and may persist in the environment. Its biodegradability is an essential consideration for its use and disposal.
Regulatory Compliance: Products containing SDS must comply with environmental regulations, which can influence their formulation and use.
LDS:
Environmental Impact: The environmental impact of LDS, including its toxicity and biodegradability, may differ from SDS. Further research is needed to fully understand these aspects, but LDS could potentially offer advantages in specific contexts.
Sustainability: LDS might be explored as a more sustainable alternative in applications where its environmental profile is more favorable.
- Performance in Specific Scientific Techniques:
SDS:
Reproducibility: SDS is widely used in scientific research due to its reproducibility and well-understood behavior in various techniques, including electrophoresis and chromatography.
Standardization: The extensive documentation of SDS ensures standardized protocols and outcomes, making it a reliable choice for scientific experiments.
LDS:
Innovative Research: LDS might be used in innovative research where its unique properties offer distinct advantages. Its performance in specific techniques might vary, and it could provide new insights or improved results in certain contexts.
Experimental Outcomes: The differing ionic properties of lithium could lead to variations in experimental outcomes, offering potential benefits in novel applications.
- Commercial and Industrial Efficiency:
SDS:
Market Presence: SDS is well-established in the market, with a broad range of applications and high availability.
Economies of Scale: The widespread use of SDS benefits from economies of scale, making it an efficient choice for many commercial and industrial processes.
LDS:
Niche Applications: LDS might be more efficient in niche applications where its unique properties are specifically beneficial. It can offer advantages in specialized formulations or products.
Market Potential: While not as widely used as SDS, LDS has the potential to carve out a market niche where its properties provide distinct benefits.
In summary, the effectiveness and efficiency of LDS and SDS depend on the specific application and context. While SDS is a well-established and reliable surfactant with broad applicability, LDS offers unique properties that can be advantageous in specialized applications. Understanding the specific requirements and performance metrics of each application can help determine the most suitable surfactant.