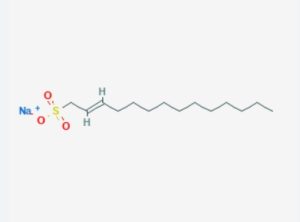
Sodium lauryl sulfate (SLS) is a versatile chemical compound widely used across various industries due to its unique chemical properties. Here are its main roles and applications in different fields:
Everyday and Industrial Applications

Detergents
SLS acts as an efficient surfactant in the detergent industry, used in the production of laundry detergents, dishwashing liquids, and other cleaning products. Its excellent cleaning and emulsifying properties make it an indispensable ingredient in detergents.

Textile Industry
In textiles, SLS is used as an intermediary between dyes and fabrics, enhancing dye penetration and uniformity for better dyeing results.
Agricultural Production
SLS is utilized in agricultural products like pesticides and insecticides.
Cosmetics and Personal Care
Foaming and Cleansing Agent
In cosmetics and skincare products, SLS serves as a foaming agent, cleanser, and wetting agent, helping products quickly interact with the skin and avoid obstruction by skin oils.

Toothpaste Foaming Agent
SLS is used as a foaming agent in toothpaste, enhancing the user experience.
Specialized Industrial Applications
Metal Flotation Agent
SLS acts as a flotation agent in metal mining, improving mineral recovery rates.
Biochemical Analysis
In biochemical analysis, SLS is a common ionic detergent used to lyse cell membranes and bind with hydrophobic membrane proteins for separation, especially in SDS-PAGE protein analysis.
Food and Pharmaceuticals

Food Additive
According to GB2760-96, food-grade SLS is a processing aid in the food industry, used in cakes, beverages, proteins, fresh fruits, fruit juices, and edible oils.
Pharmaceutical Excipient
Pharmaceutical-grade SLS is a common excipient, acting as an anionic surfactant used as a solubilizer, emulsifier, penetration enhancer, and lubricant in tablets and capsules.
Environmental Impact
Despite its widespread use, the environmental impact of SLS cannot be overlooked. It can be toxic to aquatic life, so precautions are necessary to prevent water pollution. SLS may react with other substances during water treatment, creating hard-to-degrade organic compounds that pose potential threats to water quality. To mitigate the negative environmental impact of SLS, it’s crucial to enhance environmental management and monitoring, use it responsibly, and seek alternatives.
Conclusion
The advantages of SLS lie in its multifunctionality and wide applicability. It serves as an effective cleaning agent in daily life and as an important emulsifier and dispersant in industrial production. In cosmetics and personal care products, it improves product quality and user experience. However, attention must be paid to the potential negative environmental impacts of SLS, and appropriate measures should be taken to minimize its adverse effects on the environment.