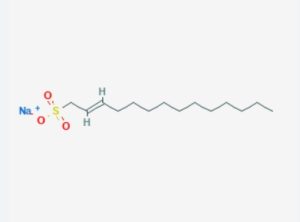
Sodium C14-16 olefin sulfonate (AOS) is a versatile and widely used surfactant in various industries, particularly in personal care products, detergents, and industrial cleaning solutions. Understanding its chemical properties, applications, and safety considerations is essential for anyone working with or using products containing this ingredient. In this article, we will delve deeply into the intricacies of sodium C14-16 olefin sulfonate, exploring its structure, functions, uses, and potential health impacts.

Chemical Structure and Properties
Sodium C14-16 olefin sulfonate is a type of anionic surfactant, characterized by its hydrophilic (water-loving) and hydrophobic (water-repelling) properties. The chemical formula for AOS can be represented as C14H29SO3Na or C16H33SO3Na, depending on the specific carbon chain length. The “C14-16” in its name refers to the range of carbon atoms in the alkyl chain, which typically varies between 14 and 16 carbons. This variability allows for different degrees of branching and straight-chain configurations, influencing the physical and chemical properties of the compound.
AOS is typically produced through the sulfonation of alpha-olefins derived from petroleum sources. The resulting product is a mixture of sulfonated olefin compounds with varying chain lengths, which are then neutralized with sodium hydroxide to form the sodium salt.
Functions and Applications
The primary function of sodium C14-16 olefin sulfonate is to reduce the surface tension between liquids and solids, making it an effective detergent and wetting agent. Its ability to create stable foams also makes it valuable in formulations requiring good foaming characteristics.
1. Detergents: AOS is commonly found in laundry detergents, dishwashing liquids, and other household cleaning products due to its strong grease-cutting abilities and compatibility with hard water.
2. Personal Care Products: In shampoos, body washes, facial cleansers, and toothpaste, AOS provides excellent foaming action and helps remove dirt and oil from the skin and hair.
3. Industrial Cleaning: Sodium C14-16 olefin sulfonate is used in industrial cleaners for degreasing metal parts, cleaning machinery, and removing stubborn stains from surfaces.
4. Agricultural Formulations: In pesticides, herbicides, and other agricultural chemicals, AOS acts as a wetting agent, improving the spread and absorption of active ingredients on plant surfaces.

Safety Considerations
Despite its widespread use, sodium C14-16 olefin sulfonate has raised some concerns regarding its safety and environmental impact:
1. Skin and Eye Irritation: Direct contact with high concentrations of AOS can cause irritation to the skin and eyes. It is recommended to wear protective gloves and eyewear when handling concentrated forms of the chemical.
2. Allergic Reactions: Some individuals may develop allergic reactions or sensitivities to AOS, leading to symptoms such as itching, redness, or rash. Products with lower concentrations of AOS are generally considered safer for sensitive skin.
3. Environmental Impact: While AOS is biodegradable under aerobic conditions, its breakdown products can persist in anaerobic environments such as landfill sites. Additionally, high concentrations of AOS in aquatic systems can lead to foam formation and potential toxicity to aquatic life.
4. Regulatory Compliance: In many countries, the use of sodium C14-16 olefin sulfonate is regulated to ensure compliance with safety standards. Manufacturers must adhere to guidelines set by organizations such as the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) in the United States and the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) in Europe.

Alternatives and Future Directions
In response to growing concerns about the environmental impact of traditional surfactants like AOS, researchers and manufacturers are exploring alternative compounds that offer similar performance while being more eco-friendly. Some promising alternatives include:
1. Alcohol Ethoxysulfates (AES): These surfactants are derived from natural sources such as coconut oil and palm kernel oil, making them more sustainable and biodegradable.
2. Methyl Esters Sulfonates (MES): MES is another biodegradable surfactant derived from renewable resources, offering comparable cleaning power to AOS but with a lower environmental impact.
3. Sugar Surfactants: These compounds are based on natural sugars and fatty acids, providing mildness to the skin while maintaining strong detergency properties.
Conclusion
Sodium C14-16 olefin sulfonate is a widely used surfactant valued for its detergent properties, foaming capabilities, and compatibility with various formulations. While it offers numerous benefits in terms of cleaning efficiency and versatility, concerns about its have led to increased scrutiny and the search for more sustainable alternatives. Users and manufacturers alike must consider these factors when choosing surfactants for their intended applications. By understanding the properties, uses, and limitations of sodium C14-16 olefin sulfonate, stakeholders can make informed decisions that balance effectiveness with environmental and human health considerations. As research continues to explore new and improved surfactants, it is likely that future innovations will provide even better solutions for both industry and consumers.