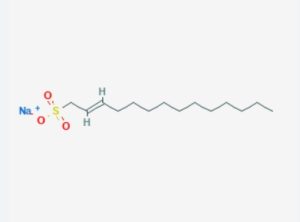
Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate (SDS) is a versatile compound with a wide range of applications across various industries. Here are several directions you can write about:
- Detergents and Cleaning Agents
SDS is a key ingredient in many household and industrial cleaning products due to its excellent surfactant properties.
Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate (SDS), also known as sodium lauryl sulfate (SLS), is a common surfactant found in a wide array of detergents and cleaning agents. Here’s an in-depth look at its role and benefits in this sector:

- Surfactant Properties:
– SDS is an anionic surfactant, meaning it has a negatively charged head and a hydrophobic tail. This dual nature allows it to reduce surface tension between water and oils or dirt, making it easier to remove grime from surfaces.
- Foaming Agent:
– One of the key characteristics of SDS is its ability to produce a rich lather. This foaming action is not only satisfying to consumers but also helps to lift dirt and grease from surfaces, enhancing the cleaning power of the product.
- Emulsification:
– SDS helps to emulsify oils and fats, meaning it disperses them into smaller droplets within the water. This prevents them from re-depositing on surfaces or fabrics and ensures they are washed away efficiently.
- Versatility:
– SDS is used in a wide range of cleaning products, including:
– Laundry Detergents: Both liquid and powder forms benefit from SDS’s ability to remove stains and oily residues from fabrics.
– Dishwashing Liquids: Its grease-cutting ability makes it ideal for breaking down food residues and oils on dishes.
– Household Cleaners: Multi-purpose cleaners often contain SDS to tackle various types of dirt and grime on different surfaces like countertops, floors, and bathrooms.
– Industrial Cleaners: In more concentrated forms, SDS is used in industrial settings to clean machinery, floors, and equipment.
- Effectiveness at Various Temperatures
SDS remains effective in both hot and cold water, making it versatile for different cleaning needs and enhancing its usability across various products.
- Biodegradability
While SDS is effective, it is also biodegradable, meaning it breaks down more easily in the environment compared to some other chemical surfactants. This makes it a more eco-friendly option for manufacturers aiming to reduce their environmental impact.
- Cost-Effective
SDS is relatively inexpensive to produce, which helps keep the cost of cleaning products down while still providing high performance.
Conclusion
Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate’s ability to act as a powerful surfactant, foaming agent, and emulsifier makes it a cornerstone ingredient in many detergents and cleaning products. Its effectiveness at various temperatures, biodegradability, and cost-efficiency further enhance its appeal, ensuring that it remains a staple in both household and industrial cleaning formulations.
- Personal Care Products
It’s commonly used in shampoos, toothpastes, and body washes, providing foaming and cleaning action.

Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate (SDS) is a prominent ingredient in a variety of personal care products, thanks to its effective surfactant properties. Here’s a deeper look into its applications in this sector:
Shampoos
SDS is commonly found in shampoos, where it serves as a powerful cleansing agent. It helps to break down oils and dirt on the scalp and hair, making it easier to wash them away. Its ability to produce a rich lather enhances the user experience, giving a feeling of thorough cleaning.

Toothpastes
In toothpastes, SDS acts as a foaming agent. This foaming action helps to distribute the toothpaste evenly throughout the mouth, ensuring that all surfaces of the teeth are cleaned effectively. Additionally, it aids in the removal of food particles and plaque, contributing to overall oral hygiene.

Body Washes
SDS is also a key component in body washes and liquid soaps. It helps to dissolve oils and grime on the skin, allowing them to be rinsed away easily. The foaming action of SDS in these products provides a luxurious lather, enhancing the sensory experience during bathing.
Facial Cleansers
In facial cleansers, SDS helps to remove makeup, dirt, and excess oils from the skin. Its surfactant properties ensure that these impurities are emulsified and washed away, leaving the skin feeling clean and refreshed. However, it’s important to note that SDS can be harsh on sensitive skin, so formulations often balance it with other ingredients to mitigate potential irritation.
Makeup Removers
SDS is used in some makeup removers to break down and emulsify makeup products, making them easier to wipe off. Its effectiveness in dissolving oils and pigments makes it a valuable ingredient in these formulations.
Considerations
While SDS is highly effective, its use in personal care products is sometimes scrutinized due to potential skin irritation, especially with prolonged or excessive use. Manufacturers often formulate products with additional moisturizing and soothing agents to counteract any harsh effects of SDS. Consumers with sensitive skin are generally advised to look for products that are specifically labeled as gentle or for sensitive skin.
In summary, SDS plays a crucial role in the efficacy and user experience of various personal care products, from shampoos and toothpastes to body washes and facial cleansers. Its ability to clean, foam, and emulsify makes it an indispensable ingredient in the personal care industry.
- Laboratory and Research
Widely used in molecular biology and biochemistry labs for protein denaturation and electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE).
Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate (SDS) is a critical reagent in laboratory and research settings, particularly in the fields of molecular biology and biochemistry. Its unique properties make it indispensable for various experimental procedures. Here’s an in-depth look at its applications in this domain:

Protein Denaturation
One of the most significant uses of SDS in the lab is for protein denaturation. SDS is an anionic detergent that binds to proteins, causing them to unfold and lose their native structure. This denaturation process is crucial for analyzing proteins in their linear form, which is necessary for many biochemical assays and techniques.
SDS-PAGE (Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis)
SDS-PAGE is a widely used technique for the separation and analysis of proteins based on their molecular weight. Here’s how SDS plays a role in this method:
Sample Preparation: Proteins are treated with SDS, which binds uniformly along the length of the polypeptide chains. This binding imparts a negative charge to the proteins, proportional to their length.
Gel Electrophoresis: The SDS-treated proteins are then loaded onto a polyacrylamide gel and subjected to an electric field. Because SDS gives all proteins a similar charge-to-mass ratio, they are separated primarily based on their size as they migrate through the gel matrix.
Visualization: After electrophoresis, the separated proteins can be visualized using various staining techniques, such as Coomassie Brilliant Blue or silver staining.
SDS-PAGE is a fundamental technique used for protein characterization, purity assessment, and molecular weight determination. It is also a preparative step in many downstream applications, such as Western blotting.
Cell Lysis and Protein Extraction
SDS is commonly used in cell lysis buffers to break open cells and solubilize cellular proteins. This is an essential step in many experimental workflows, including:
Protein Extraction: SDS helps to release proteins from cellular compartments, making them accessible for further analysis.
DNA and RNA Extraction: In nucleic acid extraction protocols, SDS aids in the disruption of cell membranes and denaturation of proteins, which helps to purify DNA or RNA.
Membrane Protein Studies
Membrane proteins are notoriously difficult to study due to their hydrophobic nature. SDS is used to solubilize these proteins, allowing researchers to analyze them in a more manageable form. This is particularly important for structural biology studies, such as X-ray crystallography and cryo-electron microscopy.
Enzyme Inhibition Studies
SDS is used in enzyme inhibition studies to investigate the effects of protein denaturation on enzyme activity. By denaturing the enzyme, researchers can study the role of protein structure in enzymatic function and identify active sites.
Considerations
While SDS is invaluable in the lab, it is important to handle it with care. SDS can be harmful if inhaled or if it comes into contact with skin and eyes. Proper lab safety protocols, including the use of gloves, lab coats, and eye protection, should always be followed when working with SDS.
In summary, SDS is a versatile and essential reagent in laboratory and research settings. Its ability to denature proteins, facilitate electrophoresis, and aid in cell lysis and protein extraction makes it a cornerstone of many biochemical and molecular biology techniques.
- Pharmaceuticals
SDS is used as an excipient in some pharmaceutical formulations to enhance solubility and stability of drugs.
Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate (SDS) plays a significant role in the pharmaceutical industry, where it is utilized for its unique properties to enhance the formulation, stability, and efficacy of various drug products. Here’s an in-depth look at its applications in this sector:

Solubility Enhancement
One of the primary challenges in drug formulation is the poor water solubility of many active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs). SDS is used as a solubilizing agent to improve the aqueous solubility of hydrophobic drugs. This enhancement in solubility can lead to better bioavailability, ensuring that the drug is more effectively absorbed by the body.
Stabilization of Drug Formulations
SDS is employed to stabilize drug formulations by preventing the aggregation of drug molecules. This is particularly important for protein and peptide drugs, which are prone to aggregation and denaturation. By stabilizing these molecules, SDS helps to maintain the therapeutic efficacy and shelf life of the drug products.
Emulsifying Agent
In pharmaceutical formulations, SDS acts as an emulsifying agent, helping to form stable emulsions. This is crucial for the preparation of various dosage forms, such as creams, ointments, and suspensions. By ensuring a uniform distribution of the drug throughout the formulation, SDS enhances the consistency and performance of the medication.
Controlled Release Formulations
SDS can be used in the development of controlled release formulations. These formulations are designed to release the drug at a predetermined rate, prolonging its therapeutic effect and improving patient compliance. SDS helps to modulate the release profile of the drug, ensuring a steady and sustained release over time.
Tablet Coating
In tablet manufacturing, SDS is used as a component of tablet coatings. These coatings can serve multiple purposes, such as protecting the drug from environmental factors, masking unpleasant tastes, and controlling the release of the active ingredient. SDS contributes to the formation of a smooth and uniform coating, enhancing the quality and functionality of the tablets.
Protein and Peptide Drugs
For protein and peptide drugs, SDS is used to prevent denaturation and aggregation during the manufacturing process. This is particularly important for biopharmaceuticals, where the structural integrity of the protein is critical for its therapeutic activity. SDS helps to maintain the native conformation of these drugs, ensuring their efficacy and stability.
Drug Delivery Systems
SDS is incorporated into various drug delivery systems to enhance the delivery and efficacy of the therapeutic agents. For example:
Micelles: SDS can form micelles that encapsulate hydrophobic drugs, improving their solubility and stability.
Liposomes: SDS is used in the preparation of liposomes, which are vesicles that can deliver drugs to specific target sites in the body, enhancing their therapeutic effect while minimizing side effects.
Considerations
While SDS offers numerous benefits in pharmaceutical formulations, its use must be carefully controlled. High concentrations of SDS can be toxic and may cause irritation. Therefore, pharmaceutical formulations are designed to use SDS at concentrations that are safe and effective for the intended use.
Regulatory agencies, such as the FDA, provide guidelines on the acceptable levels of SDS in pharmaceutical products. Manufacturers must ensure that their formulations comply with these guidelines to ensure the safety and efficacy of their products.
In summary, SDS is a valuable excipient in the pharmaceutical industry, contributing to the solubility, stability, and efficacy of various drug formulations. Its role in enhancing drug delivery and controlled release systems makes it an indispensable component in the development of modern pharmaceuticals.
- Cosmetics
SDS is found in various cosmetic products, such as makeup removers and facial cleansers, due to its emulsifying properties.

Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate (SDS) is a widely used ingredient in the cosmetics industry, known for its surfactant and emulsifying properties. It plays a crucial role in the formulation of various cosmetic products, enhancing their performance and user experience. Here’s a detailed look at its applications in cosmetics:
Makeup Removers
SDS is a key ingredient in many makeup removers due to its ability to emulsify and break down makeup products, including waterproof formulations. Its surfactant properties help to dissolve oils, pigments, and other cosmetic ingredients, making it easier to wipe them off the skin. This ensures thorough removal of makeup, leaving the skin clean and free from residues.
Facial Cleansers
In facial cleansers, SDS is used to remove dirt, oil, and impurities from the skin. Its ability to produce a rich lather enhances the cleansing process, providing a deep clean that leaves the skin feeling refreshed. SDS helps to emulsify and wash away excess sebum and environmental pollutants, contributing to clearer and healthier-looking skin.
Shampoos and Conditioners
SDS is commonly found in shampoos and conditioners, where it serves as a surfactant and foaming agent. It helps to cleanse the scalp and hair by breaking down oils and dirt, allowing them to be rinsed away easily. The foaming action of SDS provides a luxurious lather that enhances the user experience. In conditioners, SDS helps to emulsify conditioning agents, ensuring even distribution and improved hair manageability.
Body Washes and Liquid Soaps
In body washes and liquid soaps, SDS is used for its excellent cleansing and foaming properties. It helps to remove sweat, dirt, and oils from the skin, leaving it clean and refreshed. The rich lather produced by SDS enhances the sensory experience during bathing, making it a popular choice for these products.
Exfoliants and Scrubs
SDS is used in exfoliants and scrubs to aid in the removal of dead skin cells and impurities. Its surfactant properties help to emulsify the exfoliating particles, ensuring they are evenly distributed throughout the product. This provides a consistent exfoliating action that leaves the skin smooth and rejuvenated.
Toothpastes
In toothpastes, SDS acts as a foaming agent, helping to distribute the toothpaste evenly throughout the mouth. This ensures thorough cleaning of the teeth and gums, aiding in the removal of food particles and plaque. The foaming action of SDS enhances the overall effectiveness of tooth brushing.
Shaving Creams
SDS is used in shaving creams to create a stable and rich lather that softens the hair and lubricates the skin. This provides a smooth and comfortable shaving experience, reducing the risk of irritation and razor burn. The emulsifying properties of SDS help to blend the various ingredients in shaving creams, ensuring a consistent and effective product.
Considerations
While SDS is highly effective in cosmetic formulations, its use must be balanced to avoid potential irritation, especially for individuals with sensitive skin. High concentrations of SDS can strip the skin of its natural oils, leading to dryness and irritation. Therefore, cosmetic products are carefully formulated to use SDS at concentrations that are effective yet gentle on the skin.
Manufacturers often include additional moisturizing and soothing agents in their formulations to counteract any potential harsh effects of SDS. Consumers with sensitive skin are generally advised to look for products that are specifically labeled as gentle or formulated for sensitive skin.
In summary, SDS is a versatile and essential ingredient in the cosmetics industry, contributing to the cleansing, foaming, and emulsifying properties of various products. Its ability to enhance the performance and user experience of cosmetics makes it a valuable component in the formulation of makeup removers, facial cleansers, shampoos, body washes, and more.
- Food Industry
It can be utilized in the food industry as an emulsifying agent in certain processed foods.

Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate (SDS) finds applications in the food industry primarily as an emulsifying agent. Its unique properties make it valuable for improving the texture, stability, and consistency of various food products. Here’s an in-depth look at its roles and applications in this sector:
Emulsifying Agent
SDS is used as an emulsifier in the food industry to help blend ingredients that typically do not mix well, such as oil and water. This property is crucial for the production of stable emulsions, ensuring that the final product has a uniform texture and consistency. Common food products that benefit from SDS as an emulsifier include sauces, dressings, and spreads.
Processed Foods
In processed foods, SDS is used to improve the texture and mouthfeel. It helps to create a smooth and creamy consistency in products like ice creams, puddings, and whipped toppings. By stabilizing the mixture, SDS ensures that the product maintains its desired texture during storage and consumption.
Bakery Products
SDS is used in bakery products to improve the quality and shelf life of baked goods. It helps to stabilize the dough, resulting in a more uniform crumb structure and better volume in the final product. Additionally, SDS can enhance the mixing properties of dough, making it easier to handle and process.
Confectionery
In the confectionery industry, SDS is used to improve the texture and stability of various sweets and candies. It helps to create a smooth and consistent texture in products like marshmallows, nougat, and caramels. SDS also aids in the aeration process, contributing to the light and fluffy texture of certain confectionery items.
Beverage Industry
SDS is sometimes used in the beverage industry to stabilize emulsions in drinks that contain both oil and water components, such as certain flavored drinks and nutritional supplements. It helps to maintain a uniform distribution of flavors and ingredients, ensuring a consistent taste and appearance.
Dairy Products
In dairy products, SDS can be used to improve the texture and stability of items like cream, yogurt, and cheese spreads. It helps to prevent the separation of ingredients and maintains a smooth, creamy consistency. This is particularly important in low-fat and reduced-fat dairy products, where the absence of fat can lead to texture issues.
Food Additives
SDS is also used as a processing aid in the production of certain food additives. It helps to achieve the desired consistency and stability in additives that are used to enhance the flavor, texture, or appearance of food products.
Considerations
While SDS is effective in improving the texture, stability, and consistency of food products, its use in the food industry is regulated to ensure safety. Regulatory agencies, such as the FDA and EFSA, provide guidelines on the acceptable levels of SDS in food products. Manufacturers must adhere to these guidelines to ensure that their products are safe for consumption.
It’s important to note that SDS is generally used in very low concentrations in food products, and its inclusion is carefully controlled to avoid any adverse effects. Consumers with specific dietary concerns or sensitivities should always check product labels and consult with healthcare professionals if necessary.
In summary, SDS plays a valuable role in the food industry as an emulsifying agent, improving the texture, stability, and consistency of various food products. Its applications in processed foods, bakery products, confectionery, beverages, and dairy products highlight its versatility and importance in food formulation and production.
- Textile Industry
SDS is used in textile processing and finishing, aiding in the removal of oils and stains from fabrics.

Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate (SDS) is widely used in the textile industry due to its effective surfactant and detergent properties. It plays a crucial role in various stages of textile processing and finishing, contributing to the quality and appearance of the final products. Here’s an in-depth look at its applications in this sector:
Scouring
Scouring is a critical step in textile processing where impurities, such as oils, waxes, and dirt, are removed from raw fibers. SDS is used as a scouring agent to help emulsify and remove these impurities, preparing the fibers for subsequent treatments. Its strong surfactant properties ensure thorough cleaning, resulting in improved dye uptake and uniformity in the final fabric.
Bleaching
In the bleaching process, SDS is used to enhance the penetration and effectiveness of bleaching agents. By reducing surface tension, SDS allows the bleaching agents to penetrate the fibers more evenly, leading to a more uniform and brighter fabric. This step is essential for achieving the desired whiteness and brightness in textiles.
Dyeing
SDS plays a significant role in the dyeing process by ensuring even dye distribution and penetration. It helps to solubilize dyes and prevent agglomeration, resulting in more consistent and vibrant colors. SDS also aids in the removal of excess dye, reducing the risk of staining and improving the fastness properties of the dyed fabric.
Printing
In textile printing, SDS is used to improve the quality and sharpness of printed patterns. It helps to stabilize the printing paste and ensures even application of the print onto the fabric. SDS also aids in the removal of excess printing paste, preventing smudging and enhancing the clarity of the printed design.
Finishing
Textile finishing involves various treatments to enhance the properties and appearance of the final fabric. SDS is used in finishing formulations to improve the softness, smoothness, and hand feel of textiles. It helps to remove any residual chemicals and impurities, ensuring a clean and high-quality finish.
Washing and Rinsing
SDS is used in the washing and rinsing stages of textile processing to remove any remaining impurities, chemicals, and residues from the fabric. Its strong detergent properties ensure thorough cleaning, resulting in a fresh and clean final product. SDS also helps to prevent redeposition of dirt and impurities during the washing process.
Textile Auxiliaries
SDS is a key ingredient in various textile auxiliaries used throughout the processing and finishing stages. These auxiliaries include wetting agents, dispersants, leveling agents, and softeners. SDS enhances the performance of these auxiliaries, contributing to the overall quality and appearance of the textiles.
Considerations
While SDS is highly effective in textile processing, its use must be carefully controlled to avoid potential environmental and health impacts. Effluents containing SDS can contribute to water pollution if not properly treated. Therefore, textile manufacturers must implement appropriate wastewater treatment processes to minimize the environmental impact of SDS.
Regulatory agencies provide guidelines on the acceptable levels of SDS in textile effluents, and manufacturers must comply with these regulations to ensure sustainable and responsible production practices.
In summary, SDS is an essential component in the textile industry, contributing to the scouring, bleaching, dyeing, printing, finishing, and washing stages of textile processing. Its ability to remove impurities, enhance dye uptake, and improve the quality and appearance of textiles makes it a valuable ingredient in textile formulations.
- Paints and Coatings
Used as a dispersing agent in paints and coatings to ensure even distribution of pigments.
Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate (SDS) is an important additive in the paints and coatings industry, where it serves multiple functions that enhance the performance, stability, and application of various products. Here’s an in-depth look at its applications in this sector:

Dispersing Agent
SDS is widely used as a dispersing agent in paints and coatings. Its surfactant properties help to disperse pigments and fillers uniformly throughout the formulation. This ensures that the pigments are evenly distributed, preventing clumping and settling, and resulting in a consistent color and texture. A well-dispersed paint or coating provides better coverage and a more uniform finish.
Wetting Agent
As a wetting agent, SDS reduces the surface tension of the liquid components in paints and coatings. This allows the liquid to spread more easily over surfaces, improving the adhesion and coverage of the paint or coating. Better wetting ensures that the product adheres well to the substrate, enhancing its durability and performance.
Emulsifier
SDS acts as an emulsifier in water-based paints and coatings, helping to stabilize the emulsion of water and other liquid components. This stabilization is crucial for maintaining the consistency and stability of the formulation during storage and application. By preventing phase separation, SDS ensures that the paint or coating remains homogenous, providing a smooth and even application.
Foam Control
In the production of paints and coatings, foaming can be a significant issue, leading to defects in the final product. SDS can be used to control and reduce foam formation during manufacturing. By managing foam levels, SDS helps to ensure a smooth and defect-free finish, improving the overall quality of the paint or coating.
Rheology Modification
SDS can influence the rheological properties of paints and coatings, affecting their viscosity and flow behavior. By modifying these properties, SDS helps to achieve the desired application characteristics, such as ease of brushing, rolling, or spraying. Proper rheology control ensures that the paint or coating applies smoothly and evenly, without sagging or dripping.
Stabilization
SDS contributes to the stabilization of paints and coatings by preventing the agglomeration of particles and maintaining a stable dispersion. This stabilization is essential for the long-term storage and shelf life of the products. A stable formulation ensures that the paint or coating remains effective and easy to apply, even after extended storage periods.
Enhanced Gloss and Finish
In certain formulations, SDS can enhance the gloss and finish of paints and coatings. By ensuring a uniform distribution of pigments and additives, SDS helps to achieve a smooth and glossy surface. This is particularly important for high-gloss and decorative coatings, where a flawless finish is desired.
Considerations
While SDS provides numerous benefits in the formulation of paints and coatings, its use must be carefully managed to avoid potential issues. High concentrations of SDS can lead to excessive foaming or affect the viscosity of the formulation, making it difficult to apply. Therefore, manufacturers must optimize the concentration of SDS to achieve the desired balance of properties.
Environmental considerations are also important when using SDS in paints and coatings. Effluents containing SDS can contribute to water pollution if not properly treated. Manufacturers must implement appropriate wastewater treatment processes to minimize the environmental impact of SDS.
Regulatory agencies provide guidelines on the acceptable levels of SDS in industrial effluents, and manufacturers must comply with these regulations to ensure sustainable and responsible production practices.
In summary, SDS is a valuable additive in the paints and coatings industry, contributing to the dispersion, wetting, emulsification, foam control, rheology modification, stabilization, and finish of various products. Its ability to enhance the performance and application characteristics of paints and coatings makes it an indispensable component in this sector.
- Agriculture
SDS can be used in the formulation of pesticides and herbicides to improve their spread and adhesion on plants.

Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate (SDS) is utilized in the agriculture industry for its surfactant and emulsifying properties, which enhance the effectiveness and application of various agricultural products. Here’s an in-depth look at its applications in this sector:
Pesticides and Herbicides
SDS is commonly used in the formulation of pesticides and herbicides to improve their spread and adhesion on plant surfaces. As a surfactant, SDS lowers the surface tension of the spray solution, allowing it to spread more evenly over the leaves and stems. This ensures better coverage and increases the effectiveness of the active ingredients in controlling pests and weeds.
Wetting Agents
In agricultural applications, SDS acts as a wetting agent, helping to improve the penetration of water and nutrients into the soil. By reducing the surface tension of water, SDS allows it to spread more easily and infiltrate the soil more effectively. This can enhance the uptake of nutrients by plants and improve overall soil health.
Adjuvants
SDS is used as an adjuvant in agricultural sprays to enhance the performance of pesticides, herbicides, and fertilizers. Adjuvants are additives that improve the efficacy of the active ingredients in the spray solution. SDS helps to ensure that the spray droplets adhere better to plant surfaces, reducing runoff and increasing the contact time with pests or weeds.
Soil Conditioners
SDS is used in soil conditioners to improve soil structure and water retention. By enhancing the wetting properties of the soil, SDS helps to prevent soil compaction and promotes better root growth. This can lead to healthier plants and higher crop yields.
Seed Treatments
In seed treatments, SDS is used to improve the adhesion of protective coatings on seeds. These coatings can contain fungicides, insecticides, or nutrients that protect the seeds and promote healthy germination. SDS ensures that the coating is evenly distributed and adheres well to the seeds, providing consistent protection and benefits.
Foliar Fertilizers
SDS is used in foliar fertilizers to improve the absorption of nutrients through the leaves. By reducing the surface tension of the spray solution, SDS allows the nutrients to spread more evenly and penetrate the leaf surface more effectively. This can enhance the nutrient uptake and improve the overall health and growth of the plants.
Emulsifiable Concentrates
SDS is used in the formulation of emulsifiable concentrates, which are liquid formulations that can be mixed with water to form a stable emulsion. These concentrates are commonly used for pesticides and herbicides, and SDS helps to ensure that the active ingredients are evenly dispersed and remain stable in the spray solution.
Considerations
While SDS offers numerous benefits in agricultural applications, its use must be carefully managed to avoid potential environmental impacts. High concentrations of SDS can be harmful to aquatic life and may contribute to water pollution if not properly controlled. Therefore, it is important to use SDS at appropriate concentrations and implement measures to minimize runoff and environmental contamination.
Regulatory agencies provide guidelines on the acceptable levels of SDS in agricultural products and effluents, and manufacturers must comply with these regulations to ensure safe and sustainable practices.
In summary, SDS is a valuable additive in the agriculture industry, contributing to the effectiveness and application of pesticides, herbicides, fertilizers, soil conditioners, and seed treatments. Its ability to improve wetting, adhesion, and spread makes it an indispensable component in modern agricultural practices.
- Oil and Gas
Serves as a foaming agent in enhanced oil recovery processes and in drilling fluids.
Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate (SDS) is a valuable additive in the oil and gas industry, where it is utilized for its surfactant properties to enhance various processes. Its ability to reduce surface tension and stabilize emulsions makes it an essential component in a range of applications. Here’s an in-depth look at its roles in this sector:

Enhanced Oil Recovery (EOR)
Enhanced Oil Recovery (EOR) techniques are employed to increase the extraction of oil from reservoirs beyond what is possible with conventional methods. SDS plays a crucial role in several EOR processes:
Surfactant Flooding: SDS is injected into the oil reservoir along with water to reduce the interfacial tension between oil and water. This helps to mobilize the trapped oil, allowing it to flow more easily towards the production wells. Surfactant flooding can significantly improve oil recovery rates.
Foam Flooding: SDS is used to generate foam in the reservoir, which helps to improve sweep efficiency by blocking high-permeability zones and redirecting the flow of injected fluids into low-permeability zones where oil is trapped. This leads to a more uniform displacement of oil and enhances recovery.
Drilling Fluids
SDS is an important component of drilling fluids, also known as drilling muds. These fluids are used to lubricate and cool the drill bit, carry cuttings to the surface, and stabilize the wellbore.
SDS enhances the properties of drilling fluids in several ways:
Foaming Agent: SDS is used to create foam-based drilling fluids, which are particularly useful in underbalanced drilling operations. The foam helps to lift cuttings out of the wellbore and reduces the hydrostatic pressure, minimizing the risk of formation damage.
Stabilizer: SDS helps to stabilize the emulsion of oil and water in oil-based drilling fluids, ensuring that the fluid remains homogenous and effective throughout the drilling process.
Hydraulic Fracturing (Fracking)
In hydraulic fracturing, SDS is used as a surfactant to improve the efficiency of the fracturing fluid. The surfactant helps to reduce the surface tension of the fluid, allowing it to penetrate deeper into the rock formations and create more extensive fracture networks. This enhances the flow of oil and gas to the production wells.
Well Stimulation
SDS is used in well stimulation treatments to improve the flow of hydrocarbons from the reservoir to the wellbore. In acidizing treatments, SDS helps to ensure even distribution of the acid solution, enhancing its effectiveness in dissolving formation blockages and increasing permeability.
Pipeline Cleaning
SDS is used in pipeline cleaning formulations to remove deposits and residues that can accumulate in oil and gas pipelines. Its surfactant properties help to emulsify and disperse these deposits, ensuring that the pipelines remain clean and free-flowing. Regular cleaning with SDS-based formulations helps to maintain the efficiency and safety of pipeline operations.
Demulsification
In oil production, water and oil often form stable emulsions that can be difficult to separate. SDS is used in demulsification processes to break these emulsions, allowing for the efficient separation of oil and water. This is essential for meeting product specifications and reducing the water content in crude oil.
Considerations
While SDS provides numerous benefits in the oil and gas industry, its use must be carefully managed to minimize environmental impacts. Effluents containing SDS can contribute to water pollution if not properly treated. Therefore, it is important to implement appropriate wastewater treatment processes to ensure that SDS does not harm aquatic ecosystems.
Regulatory agencies provide guidelines on the acceptable levels of SDS in industrial effluents, and companies must comply with these regulations to ensure sustainable and responsible practices.
In summary, SDS is a valuable additive in the oil and gas industry, enhancing processes such as enhanced oil recovery, drilling, hydraulic fracturing, well stimulation, pipeline cleaning, and demulsification. Its ability to reduce surface tension, stabilize emulsions, and improve fluid properties makes it an indispensable component in this sector.
These uses highlight the versatility of SDS in both consumer products and industrial applications.