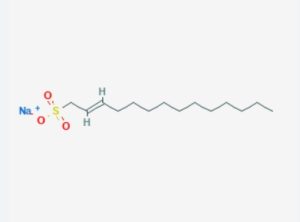
Compatibility and Interaction with Other Chemicals: Lithium Dodecyl Sulfate (LDS) vs. Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate (SDS)
When comparing Lithium Dodecyl Sulfate (LDS) and Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate (SDS), it’s essential to consider their compatibility and interaction with other chemicals. These interactions can significantly affect the performance and stability of formulations in which these surfactants are used. Here’s an in-depth exploration of their compatibility and interactions:
- Interaction with Solvents:
Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate (SDS):
Water Solubility: SDS is highly soluble in water, forming micelles at relatively low concentrations. This property makes it effective in aqueous solutions for a variety of applications.
Compatibility with Organic Solvents: SDS can interact with certain organic solvents, but its performance and solubility might vary. Typically, SDS is more effective in polar solvents.
Lithium Dodecyl Sulfate (LDS):
Solubility Characteristics: LDS also exhibits good solubility in water, but its solubility in organic solvents might differ from SDS due to the presence of lithium ions. This can be advantageous in formulations requiring specific solvent interactions.
Unique Solvent Interactions: The lithium ion in LDS might enhance or alter interactions with certain solvents, potentially leading to novel applications where traditional surfactants are less effective.
- Compatibility with Other Surfactants:
SDS:
Synergistic Effects: SDS can be combined with other surfactants, including nonionic, cationic, and zwitterionic surfactants, to create synergistic effects that enhance cleaning, emulsification, and solubilization.
Formulation Versatility: The compatibility of SDS with a wide range of surfactants makes it versatile in creating complex formulations for diverse applications, from household cleaners to industrial emulsifiers.
LDS:
Potential for Synergy: LDS might also offer synergistic effects when combined with other surfactants. The specific ionic interactions of lithium could lead to unique properties in mixed surfactant systems.
Exploratory Combinations: Research into combining LDS with other surfactants could uncover new formulation possibilities, particularly in specialized applications where unique surfactant properties are desired.
- Interaction with Polymers:
SDS:
Polymer Compatibility: SDS is commonly used with polymers in various formulations, such as in the stabilization of polymeric dispersions and emulsions. It interacts well with both synthetic and natural polymers.
Application in Emulsion Polymerization: In emulsion polymerization, SDS acts as an emulsifier and stabilizer, facilitating the formation and stability of polymer particles.
LDS:
Polymer Interactions: LDS might interact differently with polymers compared to SDS, potentially offering benefits in polymer stabilization and emulsification. The unique ionic properties of lithium could influence the compatibility and performance of LDS in polymer-based formulations.
Innovative Polymer Formulations: LDS could be explored for use in innovative polymer formulations, particularly in applications requiring specific ionic interactions or enhanced stabilization.
- Interaction with Proteins and Biochemicals:
SDS:
Protein Denaturation: SDS is known for its ability to denature proteins, making it a vital component in biochemical assays and protein analysis techniques. It binds to proteins, disrupting their native structure.
Compatibility in Biochemical Reactions: SDS is compatible with various biochemical reactions and assays, providing consistent and reliable results in protein studies.
LDS:
Unique Protein Interactions: LDS might offer unique interactions with proteins and other biochemicals due to the presence of lithium ions. These interactions could lead to new insights and techniques in biochemical research.
Potential in Biochemical Applications: The compatibility and interaction of LDS with proteins and biochemical reagents could be explored further, potentially offering new tools for protein analysis and other biochemical applications.
- Chemical Stability:
SDS:
Stable Across pH Range: SDS is chemically stable across a wide pH range, maintaining its surfactant properties in both acidic and basic environments. This stability makes it suitable for various industrial and laboratory applications.
Oxidative and Thermal Stability: SDS exhibits good oxidative and thermal stability, ensuring consistent performance under different conditions.
LDS:
Potential Stability Advantages: LDS might offer different stability profiles compared to SDS, particularly in specific pH ranges or in the presence of certain chemicals. The lithium ion could influence its chemical stability, offering advantages in specific applications.
Research on Stability: Further research on the chemical stability of LDS under various conditions could reveal new applications and benefits, particularly in environments where SDS might be less effective.
- Interaction with Metals and Ions:
SDS:
Metal Ion Interactions: SDS interacts with metal ions, which can influence its performance in formulations. These interactions must be managed to ensure the desired performance in applications such as detergents and cleaners.
Chelating Effects: SDS can sometimes act as a chelating agent, interacting with metal ions and affecting their availability in solutions.
LDS:
Lithium Ion Influence: The presence of lithium ions in LDS might lead to unique interactions with other metals and ions. This could influence the performance of LDS in formulations where metal ion interactions are critical.
Ion-Specific Applications: LDS’s interaction with metal ions could be explored for specific applications, such as in metallurgical processes, water treatment, or specialized cleaning formulations.
- Compatibility in Pharmaceutical Formulations:
SDS:
Drug Solubilization: SDS is used in pharmaceutical formulations to enhance the solubility and bioavailability of poorly soluble drugs. Its interaction with drug molecules can improve their therapeutic efficacy.
Pharmacokinetic Compatibility: SDS is compatible with various drug delivery systems, providing consistent performance in enhancing drug solubility and absorption.
LDS:
Pharmaceutical Potential: LDS might offer unique advantages in pharmaceutical formulations, particularly where lithium’s properties can enhance drug solubility or stability. The specific interactions of LDS with drug molecules could open new avenues in drug delivery research.
Innovative Drug Formulations: The compatibility of LDS in pharmaceutical applications could lead to innovative drug formulations, particularly for drugs that benefit from lithium’s unique ionic properties.
In summary, while SDS is a well-established surfactant with broad compatibility and interactions with various chemicals, LDS offers unique properties that could lead to new and specialized applications. Understanding the specific compatibility and interactions of LDS and SDS with other chemicals helps in selecting the appropriate surfactant for optimal performance in different formulations and applications.