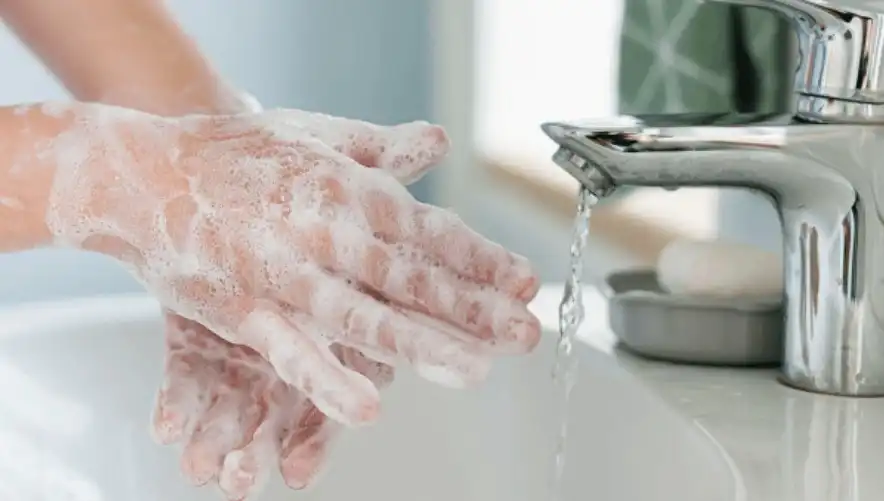
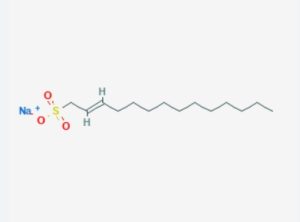
Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate (SDS), also known as Sodium Lauryl Sulfate (SLS), is a key ingredient in hand washing fluids and soaps due to its surfactant properties. Its applications in hand washing fluids include:
1. Cleansing Agent: SDS acts effectively to remove dirt, oils, and microorganisms from the skin. By reducing the surface tension of water, it enables the hand washing fluid to spread more easily over the hands and penetrate the small crevices where pathogens may reside.
2. Foaming Agent: One of the most noticeable roles of SDS in hand washing fluids is its ability to create foam. This foam is not only satisfying for the user but also practical, as it helps lift dirt and microbes from the skin for easier rinsing away.
3. Emulsifying Agent: SDS helps in emulsifying the dirt and oils present on the skin, making them mix with water. This action allows for the thorough removal of substances that are typically water-insoluble.
4. Thickener and Texturizer: In some formulations, SDS contributes to the overall viscosity and texture of the hand washing fluid, providing a richer and more luxurious product consistency.
5. Solubilizer: It aids in solubilizing other ingredients in the hand wash, such as fragrances, essential oils, or moisturizers, ensuring they are evenly dispersed throughout the product.
Despite its widespread use due to these beneficial properties, SDS/SLS has been noted for its potential to cause skin irritation in sensitive individuals, especially with frequent use. It can strip natural oils from the skin, leading to dryness or irritation. As a result, there is a growing market for SDS-free hand wash products that use milder surfactants aimed at reducing the risk of skin irritation while still providing effective cleaning properties. Manufacturers often balance the inclusion of SDS with skin conditioning agents or opt for alternative surfactants to cater to the needs of consumers with sensitive skin.